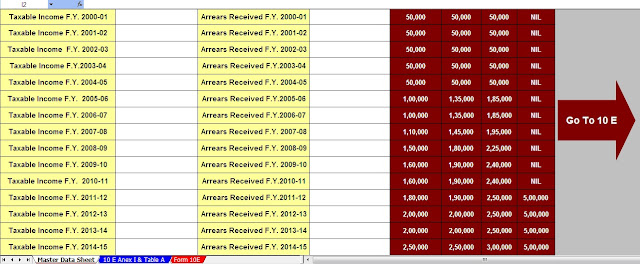
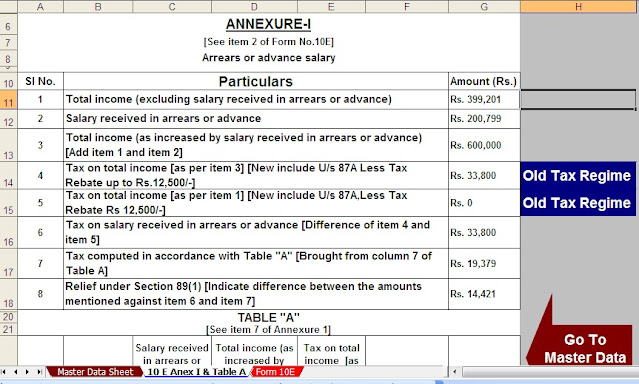
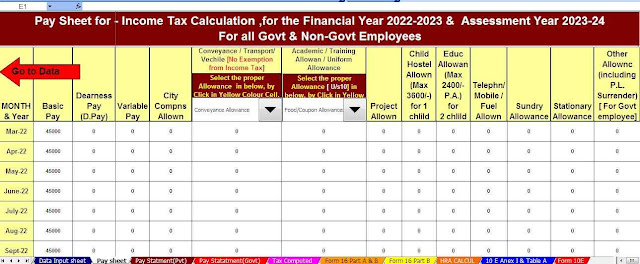
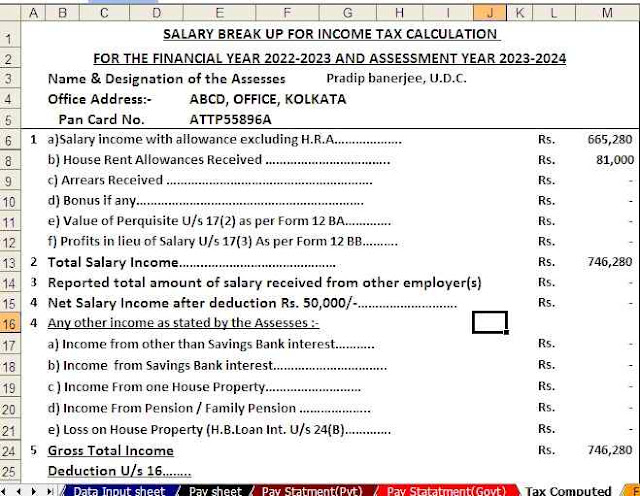
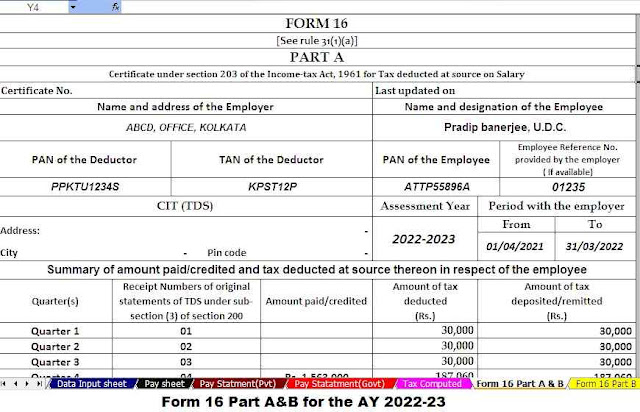
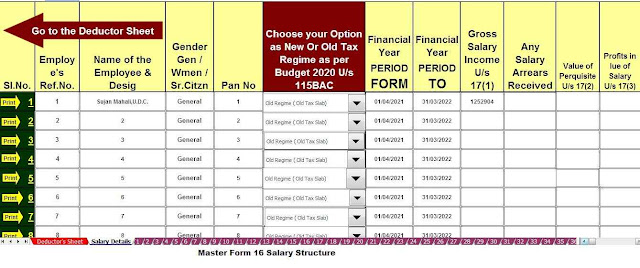
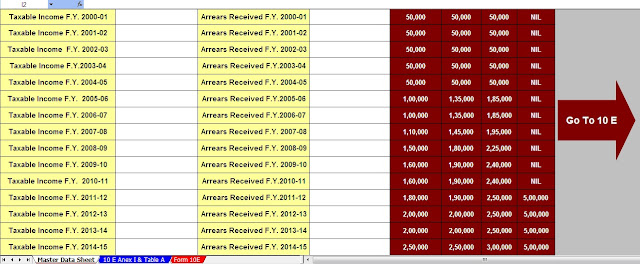
Housing Loan Interest Deduction - Section 24B| Section 24b of the Income Tax Act allows for the
deduction of interest on mortgage loans from taxable income. The said loan must be taken for the
purchase or construction or repair or reconstruction of residential property.
This deduction is allowed on an
accrual basis, not the payment. In other words, interest due for the year is
allowed as a deduction whether or not it is paid.
The deduction may be claimed for
two or more home loans. The deduction may also be claimed for two or more
households.
To claim the deduction under this
section, a person must own the house and the loan must also be in his or her
name.
Interest inclusions/exclusions
Interest includes service fees,
brokerage, commission, prepayment fees, etc.
Interest/fines on unpaid interest will
not be allowed as a deduction.
Type of loan for which the
deduction is allowed
The deduction will be allowed
regardless of the nature of the loan, whether it is a home loan or a personal
loan from any person/institution. The loan must be used for the construction,
purchase or repair/reconstruction of the house.
If a person, instead of taking out
a loan from a third party, pays the sale price to the seller in instalments
with interest, then that interest is also allowed.
Maximum deduction limit
These deduction limits apply per
appraised and not per property. Therefore, if a person owns two or more homes,
the total deduction for that person remains the same.
1) On rented property / Considered
leased - Rs. 2 million
2) Self-Occupied House (SOP) - Rs.
2 million
Interest in the
pre-construction/acquisition period
Pre-construction/acquisition period
interest is allowed in five equal instalments from the year of completion of
home ownership. This deduction is not allowed if the loan is used for repairs,
renovations or reconstruction.
The pre-construction/acquisition
period begins on the loan date and ends on the last day of the previous fiscal
year in which construction is completed.
Deduction in case of co-borrower
If the mortgage loan is taken
together, the deduction is allowed to each co-borrower in proportion to his
share of the loan. To make such a deduction it is necessary that the said
co-borrower is also co-owner of that property. If the beneficiary is a co-owner
but is paying off the entire loan, he or she can claim the deduction of the
entire interest paid by the beneficiary.
The deduction limit in the case of
Autonomous Property is applied individually to each co-borrower. In other
words, each co-borrower can claim a deduction of up to Rs. 2 lakhs/Rs. 30,000.
No limits apply to the leased property.
Interest deduction with HRA
The HRA pursuant to section 10(13A)
and the interest deduction may be used simultaneously, even if the home
owner is in the same city where you reside in a rental property.
Form 12BB must be filed with the employer if you want your employer to consider a deduction under this section and therefore deduct lower TDS