Section 10 Income Tax Act | Under the Income Tax Act, 1961, any citizen of
exceeds a certain threshold is liable to pay taxes. Therefore, when collecting each fiscal year, taxpayers
look for ways to minimize their tax liability.
To ease the burden on taxpayers by encouraging them to save, invest, and pay taxes, the law listed some income as tax-exempt.
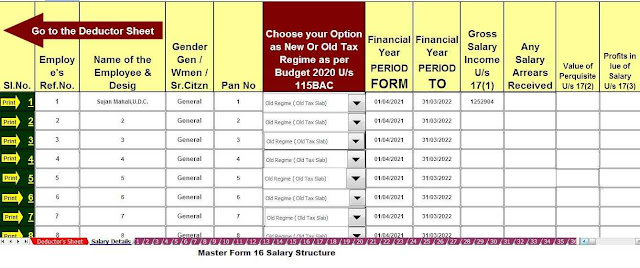
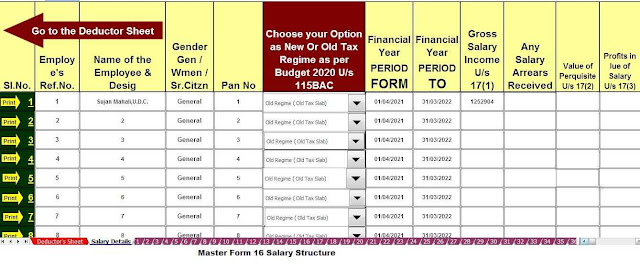
Download and prepare at a time 50 Employees Form 16 Part B for the F.Y.2021-22
Deduction under Section 10 of the Income Tax Law
Exemption from the category of sections and subsections
10 (1) Agricultural income of the self-employed No tax
10 (2) Income of a Hindu family member is indivisible Without tax
10 (10C) Voluntary Retirement Benefit Exempt up to Rs. 5 lakh
10 (10D) Life insurance claims including bonus No tax
10 (11) (12) Amount withdrawn from the pension fund Without tax
10 (10BC) State Disaster Damage Compensation No tax
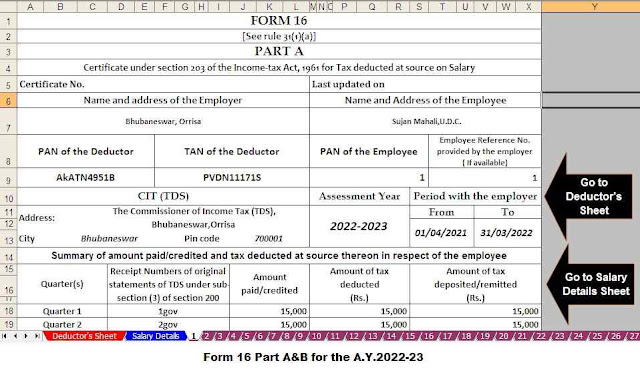
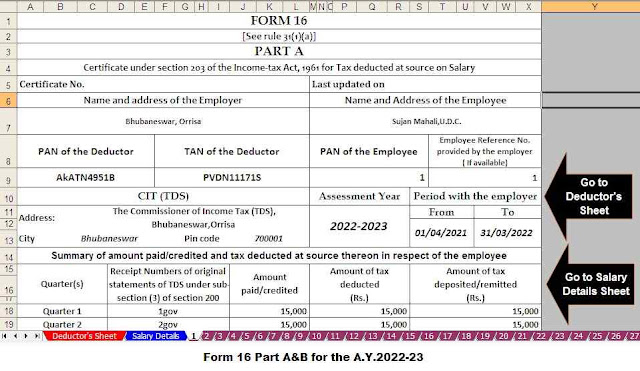
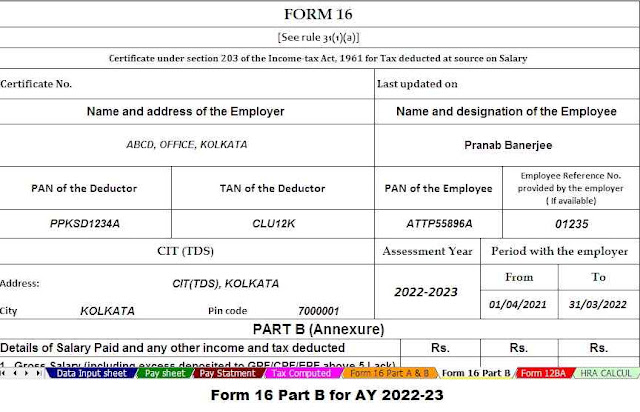
Download and prepare One by One Income Tax Form 16 Part A&B and Part B for the F.Y.2021-22 in Excel
10 (13A) Rental Housing Benefit (HRA) At a minimum, the following are exempt: Actual HRA 40% of salary or 50% of salary if you live in metropolitan areas Rent paid less than 10% of salary
10 (15) Income from securities not taxed not taxed
Other exclusions under section 10
Employees receive a number of benefits in addition to their regular income. Most of these benefits are considered part of general income, and some are exempt under Section 10.
Download and prepare at a time 50 Employees Form 16 Part A&B for the F.Y.2021-22
1. Special compensation under section 10 (14):
Some allowances are classified as special benefits under Section 10 and are tax-free. The exception depends on the amount allowed or the money actually used for a particular purpose, whichever is less.
Grants under subsection (14) of section 10 of the Income Tax Act include:
2. Per diem: includes per diem provided to cover expenses incurred during a business trip or when moving/moving to a new job.
3. Travel Allowance: Provided to employees to cover travel expenses during official travel or when moving to another job. Including expenses incurred in connection with the transfer of personal belongings, etc.
Download and prepare at a time 100 Employees Form 16 Part B for the F.Y.2021-22
4. Adjutant's allowance: This exemption applies to the salary of an assistant assigned to assist in the performance of official duties.
5. Uniform allowance: Where the office requires you to wear a uniform while on duty, an allowance is offered to cover the cost of purchasing and maintaining a uniform.
6. Travel expenses: This subsidy is provided to cover expenses related to official travel. It does not cover travel expenses from home to work.
7. Research or Academic Scholarship: This exception is provided by educational and research institutions to encourage research or academic training, education, etc.
8. U/S 10(14)(i) exemption: -
A) Per Diem
B) Travel allowance
9. Specific compensation under Article 10(14)(ii):
Compensation excluded pursuant to paragraph (14)(ii) of Section 10 of the Income Tax Act
• Weather benefits: including compensation for work in the highlands or hills.
• Up to 800 for the hills of Himachal Pradesh,
• Discount up to 7000 per month for Siachen.
• Discount up to 300 for other high altitude locations.
• Tribal Areas Allowance: 200 grants for those working in tribal areas, registered or pre-classified agencies such as Karnataka, West Bengal,
• Border Area Benefits: Pursuant to section 10(14)(ii) 2BB, military personnel serving in border areas, remote areas, or disturbed areas receive benefits ranging from 200 to 1,300 per month.
Download and prepare at a time 100 Employees Form 16 Part A&B for the F.Y.2021-22
• Compensation in the field: a grant of 2600 per month is permitted under section 10(14)(ii) provided that it is given to individuals for tasks in unusual areas.
• Children's Education Fund: Exceptions to Section 10(14)(ii) are available for a benefit of Rs.100 per child for up to 2 children. Boarding allowance can also be claimed in the amount of 300 / month/child up to 2 children.
• Counterinsurgency allowance: The Section 10(14)(ii) allowance of $3,900 per month is for those who work in the armed forces in counterinsurgency.
• Island Service Allowance: An exemption under Section 10(14)(ii) of 3250 per month for military personnel serving in the Andaman and
• Other benefits under paragraph (14) (ii) of Section 10 of the Income Tax Act include:
• 800/month for underground miners.
• 4,200 per month for employees in high activity areas.
• 1000 per month for workers in certain modification areas.
• 3,200 per month in travel allowance for employees travelling between home and work