Section 80DD Tax Exemption for the People with Disabilities as per Budget 2022 | The
Finance Act 2022 proposes an amendment to section 80DD to specify that the deduction will
also be allowed when the scheme pays an annuity or lump-sum payment to a beneficiary
who is a disabled dependent of the person during the life of the person upon reaching the
age of 60. the individual and the individual stop paying the fee or premium under the scheme.
Section 80DD allows a deduction to be made to a resident individual for filing an amount with an insurance scheme if the scheme pays an annuity or lump-sum payment to a beneficiary who is a dependent of that individual with a disability in the event of that individual's death.
This deduction is not allowed if the scheme provides for an annuity or lump-sum payment to a beneficiary who is a dependent of that person with a disability during that person's life.
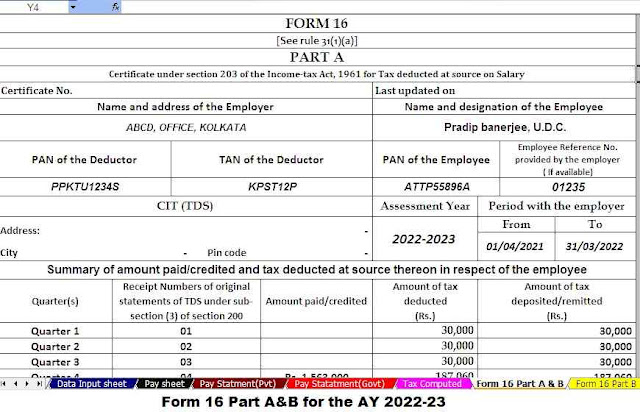
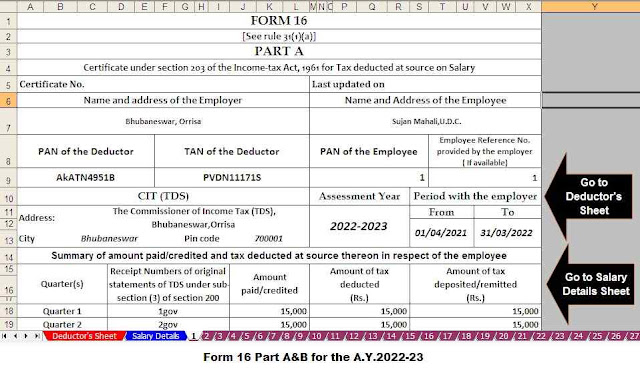
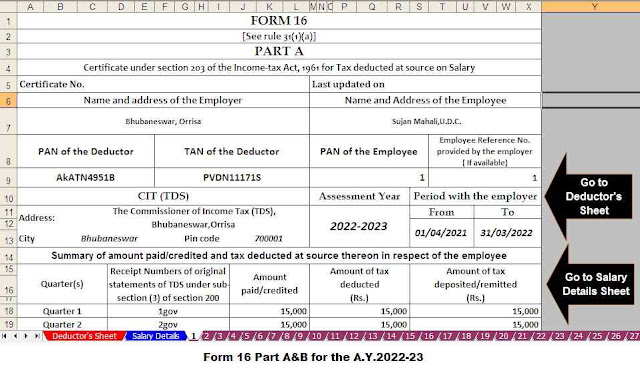
Download and Prepare at a time 50 Employees Form 16 Part A&B for the Financial Year 2021-22
During the presentation of the union budget for 2022, Minister of Finance Nirmala Sitaraman announced the weakening of tax benefits for a person when an insurance company pays an annuity to a disabled beneficiary during the life of the applicant.
He stated that a parent or guardian of a person with a disability can take out insurance for that person. This law provided for a deduction to a parent or guardian only if the capital or annuity benefit was available to the disabled person after the death of the subscriber, parent or guardian.
There may be situations where dependents with a disability may be required to pay an annuity or a lump sum even while their parents/guardians are alive.
He proposed to allow the payment of an annuity and a one-time allowance for disabled dependents during the life of parents/guardians, or for parents/guardians who have reached the age of sixty.
To this end, section 21 of the Treasury Act 2022 amends the current provisions of section 80DD as follows:
Change section 80DD.
21. In section 80DD of the Income Tax Act, effective April 1, 2023——
(I) in paragraph (2) of paragraph (a), the following paragraph is replaced, namely:
"(A) The regime referred to in subparagraph (b) of paragraph (1) provides for the payment of an annuity or a lump sum to a dependent as a person with a disability -
(i) in the event of the death of a person or member of an undivided Hindu family on whose behalf the accession to the regime was effected; or
(ii) After such individual or undivided member of a Hindu family reaches the age of sixty years or older and the payment or deposit under such scheme has been stopped; "
Download and Prepare at a time 50 Employees Form 16 Part B for the Financial Year 2021-22
Explanation of amended provisions
Paragraph 21 seeks to amend section 80DD of the Income Tax Act regarding the deduction for alimony, including the treatment of a dependent who is disabled.
The provisions of this section, inter alia, provide for a deduction to the benefit of a person or an integral Hindu family residing in India from expenses incurred for the treatment (including care), education and rehabilitation of a dependent of a person with a disability; or the amount paid to a life insurance company (LIC) or any other specified insurer, administrator or company in connection with a disabled dependent support scheme.
Paragraph (2) of the same paragraph provides that the deduction is allowed only if the payment of annuity or capital is made in favour of a dependent, disabled person, in the event of the death of an individual or a family member. The Hindu on whose behalf she has signed up for this scheme and the commissioner nominates either the dependent or any other person to collect payment on her behalf for the benefit of the disabled dependent. Paragraph (3) of this section provides that if the burden of disability precedes a person or member of a Hindu undivided family, the amount deposited under this scheme shall be deemed to be the valuer's income for the previous year in which that amount was received by the valuer. to the check and will therefore be taxed as income for the previous year.
Download and Prepare at a time 100 Employees Form 16 Part A&B for the Financial Year 2021-22
It is proposed to replace paragraph (a) of paragraph (2) of this section to provide that the deduction specified in paragraph (b) of paragraph (1) of this section is allowed if the regime provides for the payment of an annuity or a lump sum in favour of a dependent, a person with a disability, in the event of the death of the natural person or undivided member of the Hindu family in whose name the registration was made; or upon reaching the age of sixty years or more of a Hindu undivided family member, and the payment or deposit under such scheme has ceased.
It is also proposed to include a new paragraph (3A) providing that the provisions of paragraph (3) do not apply to the amount received by the defendant as incapacitated prior to his death from an annuity or lump sum payment on the application of the condition referred to in proposed paragraph (ii) of paragraph (a) of paragraph (2).
These amendments will come into effect on April 1, 2023, and will therefore apply to the 2023-2024 assessment years and subsequent assessment years.
Existing Section 80DD Provisions: Before Changes Proposed by Treasury Act 2022
The present provision of section 80DD, inter alia, provides for a deduction for an individual or HUF resident in India in respect of (a) medical expenses (including care), education and rehabilitation of a dependent person who is a person with a disability; or (b) the amount paid to the LIC or any other specified insurer, director or company in connection with a disabled dependents scheme.
2. Paragraph 2 of the aforementioned paragraph provides that a deduction is allowed only if the payment of annuity or capital is made in favour of a dependent person, in the event of the death of the person or member of the HUF on behalf of whom the entry was completed so that the regime was completed.
3. Paragraph (3) of the above article provides that if the disabled person is near death to an individual or a member of the HUF, the amount deposited with that body shall be deemed to be the appraiser's income in the previous year in which that amount was received by the appraiser for verification and therefore, will be taxed as income for the previous year.
4. Paragraph (4) of the above section provides for the delivery of a copy of the medical certificate in the prescribed forms and methods (see Rule 11A) to claim the deduction specified in this section, together with the return of income referred to in section 139, in respect of the year of assessment for which deduction is requested.
Download and Prepare at a time 100 Employees Form 16 Part B for the Financial Year 2021-22
Section 80DD was introduced by the Treasury Act 1998, replacing and merging then Section 80DD and Section 80DDA.
It was felt that parents or guardians of disabled dependents might not be required to bear annual medical expenses for disabled dependents.
However, the parent or guardian will always feel the need to provide future support for the disabled dependent. Section 80DD has been enacted to provide a parent or guardian with a choice of medical expenses or the future needs of a disabled dependent, as the case may be. With this provision, a parent or guardian can claim a deduction of Rs. 75,000/Rs. 1.25.000 for the treatment and future needs of a dependent disabled person in the manner most appropriate to their needs.
The Finance Act 1998 allowed a deduction of up to Rs. 40,000 under section 80DD. The Finance Act 1999 amended the provisions of this section to provide for a one-time deduction of Rs. 40,000, regardless of actual expenses. This was done to eliminate the difficulty in providing actual proof of expenditure. The 1999 Financial Memorandum Bill states: “There were reservations that this provision, as it stands, could create difficulties for such appraisers, as it could lead to a situation where appraisers might need proof of such expenses. such discomfort to the guardians of the disabled person is proposed to allow a deduction of Rs 40,000/- in such cases.
Download and Prepare One by One Form 16 Part A&B and Part B for the Financial Year 2021-22