Download Automated Income Tax Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) with Form 10 E for the
F.Y.2021-22 with details of Section 80TTA of the Income Tax Act
Download Automated Income Tax Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) with Form 10 E for the F.Y.2021-22.What is Section 80TTA?
As per the Income Tax Act Under Section 80TTA provides for an Exemption for interest income from Bank/Post Office. Discounts are available with a few limitations and limitations. In this article, we have covered everything about claiming a tax deduction because of the interest earned
Tax exemption on interest income
Where the total income of a taxpayer includes any income through interest on the deposit, such income is tax-free. The taxpayer must be an individual taxpayer, a member of a Hindu undivided family, or a member of a Hindu undivided family.
The way to earn interest should be from a deposit with a savings account:
A banking institution where the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 (10 of 1949), applies
A cooperative society is involved in the banking business.
The assessee can claim a tax deduction when calculating his total income
Tax deduction on the interest income from the time deposit is not available.
Therefore, the exemption is not allowed in the following cases:
Interest from fixed deposits
Interest from recurring deposits
No other time deposit
The amount of deduction under section 80TTA of the Income-tax Act
The maximum discount allowed under 8TTA for a financial year is Rs.
Actual interest is discounted if the total interest is less than Rs.
If the total interest is excess than Rupees Ten Thousand, only Rupees Ten Thousand is entitled as tax exemption
The assessee must consider his / her total interest from all savings bank accounts.
Eligibility to claim an exemption under 80TTA
Cutting approved under 80TTA
The below-given taxpayers can be entitled to get the benefits under Section 80TTA of the Income Tax Act:
Private Taxpayer or Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
Indian residents
Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) own NRO Savings Accounts
Deduction under 80TTA is unauthorized
The following types of taxpayers are not eligible for deduction:
Interest income is received from any deposit in a savings account. The account is owned by or on behalf of:
A firm, or
An association of individuals, or
A body of individuals
Then no exemption will be given to any partner of the firm or any member of the association or any person of the body. These taxpayers will not be allowed to deduct against interest income when calculating total income.
Furthermore, even senior citizens cannot claim a waiver under the 80TTA. They can claim tax benefits under 80TTB.
How to claim Section 80 TTA exemption while filing an income tax return?
First, you add the interest income with your total income. You will then have to claim tax benefits under section 80 deduction under section 80TTA.
Income Tax Section 80TTB only for Senior Citizen above 60 years of age.
Where the total income of a taxpayer includes any income through interest on the deposit, such income is tax-free.
Ways to earn interest on deposits with:
A co-operative society is engaged in conducting banking business.
A post office under the Indian Post Office Act, 1898
The assessee can claim a tax deduction when calculating his total income
A maximum of Rs 50,000 was approved by 8TTB for a financial year.
If the total interest is less than Rs. 50,000, the actual interest is discounted.
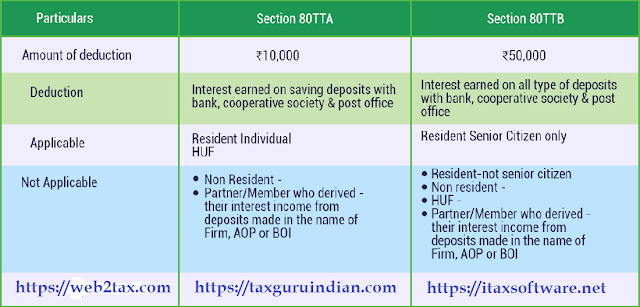
The difference between Section 80TTA and 80TTB
Section 80TTA Section 80TTB
Individual Taxpayer and Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) only allowed for senior citizens above 60 years of age
Interest earned on deposits with savings account only: - Deposit with a savings account - Fixed deposit, term deposit or recurring deposit
Exemption limit under section 80TTA Rs.10,000 per annum Exemption limit under section 80TTB Rs.50,000 per annum
Download Automated Income Tax Arrears Relief Calculator U/s89(1) with Form 10 E for the F.Y.2021-22