Income tax planning. Planning of proper Tax savings is almost indispensable for the F.Y.2021-22
Although tax evasion is difficult, you can still have effective tax evasion strategies
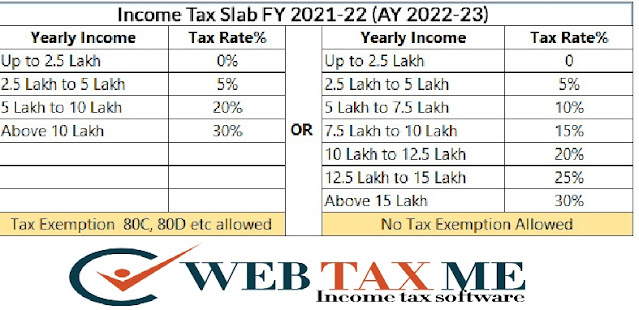
Two important steps
1) Choose between the old tax (with deduction) and the new system of governance (without exemption)
One has to analyze carefully and compare the tax deduction and consider other factors to choose between the two.
2) inform your employer (so they have to deduct TDS based on your choice)
Tax Saving Tips: -
1. Additional tax savings with NPS under section 80CCD
In addition to deductions under Section 80C of Rs 1.5 lakh per annum, you can claim additional tax exemption under Section 80CCD (1B) with an additional 80% grant. 50,000 in your NPS account.
Example: -
If the taxpayer is subject to% 0% tax, then additional tax benefit =
50000 * 30% = 15,000 + 4 Education cess = Rs. The amount of tax is 15,600.
2. House rent allowance
Who lives in a rented home, and then you can help save tax through HRA. The maximum amount of HRA discount: - Less of the following
a) Obtained actual HRA
B) 40% (Non Metro) / 50% (Metro) (Basic Salary + DA)
c) 10% less than actual rent (basic salary + DA)
Note: - If you rent a house and pay more than Rs 1 lakh per annum - do not forget to provide the landlord's PAN to claim an HRA discount.
A clear reading of Circular No. 01/2019 dated 01 January 2019 and Form 12BB proposes that a limit of Rs. 1 lakh is applicable for each landlord.
Download Automated Income Tax House Rent Exemption Calculator U/s 10(13A) in Excel.
If you pay rent for a residential home + do not receive an HRA from your employer + you or your spouse or your minor child does not currently own a residential home where you live
You can then claim a deduction under section 80GG.
Minimum cuts under this section will be considered as:
A. 5,000 per month;
B. 25% of total gross income *;
C. 10% less than the actual income including actual rent (ATI)
ATI = Total income less short term capital gain, short term capital gain under section 111A and income under section 115A or 115D and deduction from 80C to 80U (excluding deduction under section 80GG)
3. Child Education Allowance:
Maximum discount. 2 children (Rs. 100 per month)
4. Employees are provided free food and drink:
It can also be given in the form of food/food coupons to employees like Sodexo.
Amount discount up to Rs 50 per meal.
Example = Eat 25 working days a month and 2 meals a day
Discount amount = 25 * 50 * 2 = 2,500 per month
5. Hostel Expenses Allowance:
Maximum discount. With 2 children (Rs. 300 per month)
6. Leave Travel Allowance (LTA): -
Discounts are only available for travel expenses (the employee is going anywhere in
Exemptions are only available at actual travel costs, such as air, rail or bus fares charged by the employee.
Discount is available only due to submission of expenditure bill.
7. Employer's Contribution to PF and NPS: -
Employer's contribution to NPS and EPF is tax-free up to 12% of basic salary.
8. Standard deduction
For all salaried individuals, a standard discount of Rs 50,000 is available.
9. Employment / Professional Tax: -
The amount paid in a year is deductible.
10. Exemption under section 80C
The most popular and it allows discounts up to Rs 1.5 lakh. The taxpayer may deposit in PF, ELSS, FD, NSC, NPS, Life insurance. Apart from that, one can also claim the basic payment of a home loan, tuition fee and stamp duty under this section.
11. Exemption under section 80D
This department offers a discount for medical insurance premiums paid for oneself, family and parents.
People under the age of 60 can claim Rs 25,000 for themselves and their families and Rs 25,000 for their parents (if they are under 60).
12. Discount for interest on the second 80E of education loan
Interest paid on loans taken for the higher education of oneself, wife or children can be claimed on a real basis.
13. Section 24(B) - Interest on home loan deduction
It offers a discount of interest on home loans up to Rs 2 lakh for self-occupied houses and houses that will be vacated, there is no limit to claim interest discount.
14. Section 80EEA- For first-time homeowners
This section offers a discount of Rs 1.5 lakh, which means you can technically increase the upper limit for self-occupied houses to Rs 3.5 lakh (deduction of interest on the home loan which will be more than the discount available under section 24).
15. Section 80TTA tax savings on interest earned in a savings bank account.
Interest earned- Post Office Savings Account of Bank Savings Accounts Cooperative Society.
The maximum discount limit under this section is Rs. 10,000
80TTB: - Senior citizens can claim up to Rs 50,000 as tax exemption.
16. Tax savings on repayment of an education loan under section 80E: -
You will get tax benefit on the interest component of the loan taken for higher education and there is no limit.
Paying interest could be a parent or student.
Taxpayers can claim a tax deduction for up to 8 fiscal years from the year of commencement of interest payments on the education loan, or until full interest is paid, whichever is earlier.